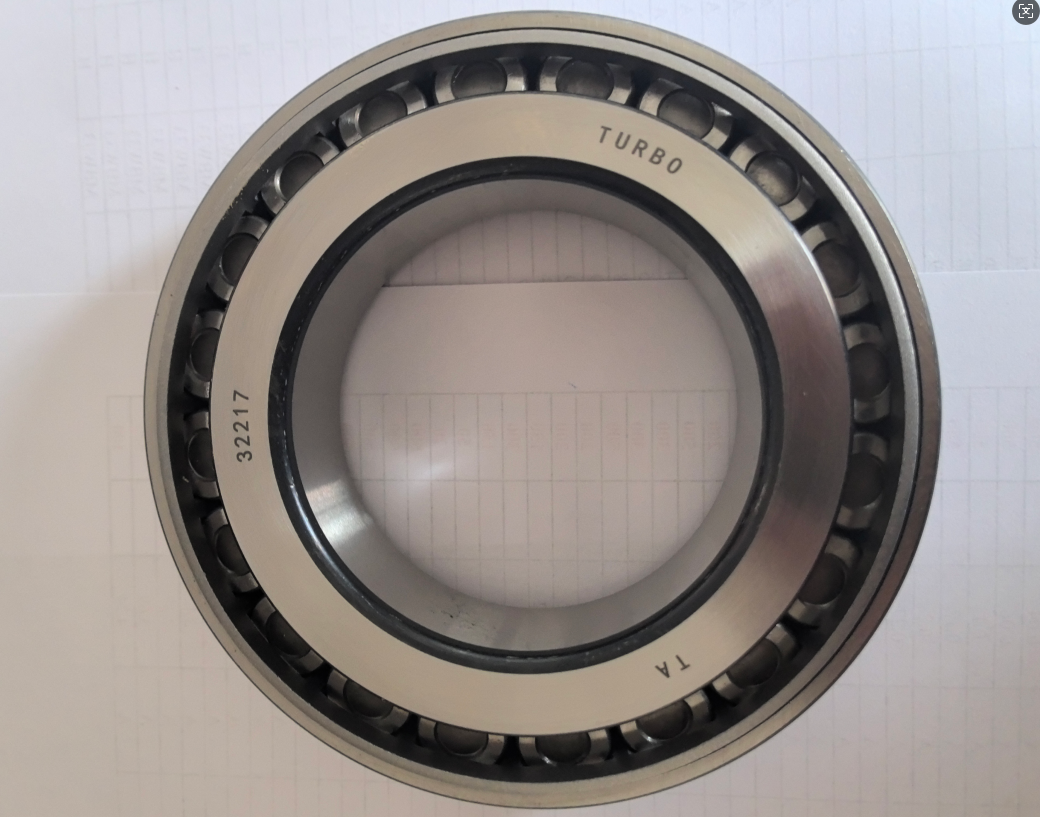
The 32217 bearing is a very common tapered roller bearing. Here is a detailed introduction to its key information:
1. Basic Type and Structure
- Type: Tapered roller bearing. This type of bearing is designed to withstand both radial loads (forces perpendicular to the shaft) and large unidirectional axial loads (forces along the shaft direction).
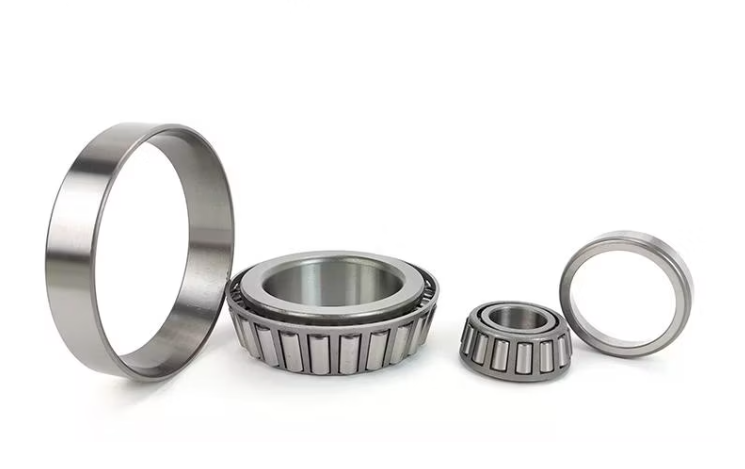
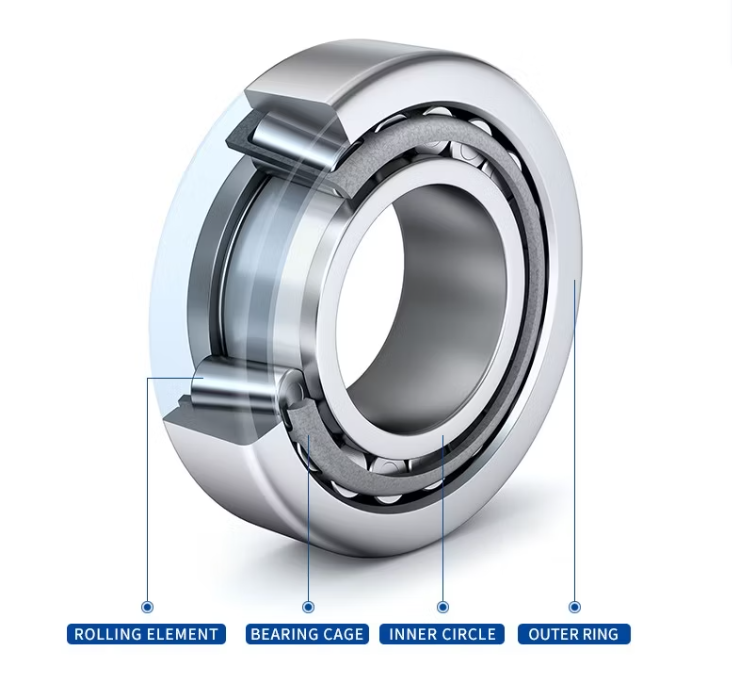
- Structure: It consists of four main components:
- Inner ring: A cone with a tapered raceway, mounted on the shaft.
- Outer ring: A cup with a tapered raceway, installed in the bearing housing.
- Tapered rollers: Frustum-shaped rolling elements that roll between the raceways of the inner and outer rings. The rollers are usually precisely guided and separated by a cage.
- Cage: Typically made of stamped steel, turned brass, or engineering plastics, it is used to evenly separate the rollers and reduce friction and wear.
2. Model Interpretation (ISO Standard)
- 32217:
- 3 : Represents a tapered roller bearing.
- 22 : Represents the dimension series. Specifically:
- Width series: 2 (medium width)
- Diameter series: 2 (medium diameter)
- 17 : Represents the bore diameter code. For bearings with a bore diameter ≥ 20mm, the bore diameter = 17 × 5 = 85 mm.
3. Main Dimensions (Standard Values)
- Bore diameter (d): 85 mm
- Outer diameter (D): 150 mm
- Width/height (T/B/C): 39 mm (This is the total width/height of the bearing, i.e., the distance from the large end face of the inner ring to the large end face of the outer ring. Sometimes the inner ring width B and outer ring width C are also marked, but T is the most commonly used overall width parameter).
- Inner ring width (B): Approximately 39 mm (usually the same as or close to T; refer to the specific dimension table for details).
- Outer ring width (C): Approximately 32 mm (refer to the specific dimension table for details).
- Inner ring small rib diameter (d₁ ≈): Approximately 104.5 mm (for installation calculation).
- Outer ring small rib diameter (D₁ ≈): Approximately 130 mm (for installation calculation).
- Contact angle (α): Usually between 10° and 18°, the specific value should be checked in the bearing manufacturer’s catalog. The contact angle determines the axial load-carrying capacity.
- Fillet radius (r min): Generally, the minimum fillet radius of both the inner and outer rings is 2.1 mm (during installation, attention should be paid that the fillet of the shaft shoulder and the bearing housing shoulder should not be smaller than this value).
4. Main Performance Characteristics
- High load-carrying capacity: Especially strong in withstanding unidirectional axial loads, and can also bear large radial loads. The rollers are in line contact with the raceways, resulting in good load distribution.
- Separability: The inner ring assembly (inner ring + rollers + cage) and the outer ring can be installed independently, which is very convenient for installation, adjustment, and maintenance.
- Need for paired use: Since it can only bear unidirectional axial loads, in occasions where bidirectional axial loads need to be borne or precise axial positioning of the shaft is required (such as shafting), the 32217 bearing usually needs to be used in pairs (face-to-face, back-to-back, or tandem configuration), and the clearance is adjusted through preloading.
- Adjustable clearance: By adjusting the axial relative position between the inner and outer rings, the internal clearance of the bearing or the preload can be easily adjusted to obtain the best rigidity, rotation accuracy, and service life.
- Rotational speed: The limiting speed is usually lower than that of deep groove ball bearings, but it can still meet the needs of most industrial applications. The specific limiting speed depends on the lubrication method, load, cage type, etc.
- Friction and temperature rise: The friction coefficient is slightly higher than that of ball bearings, and the temperature rise during operation may be slightly higher.
5. Installation Precautions
- Paired use: As mentioned earlier, it is usually installed in pairs.
- Adjust clearance/preload: After installation, the axial position must be carefully adjusted to achieve the designed clearance or preload. This is crucial for bearing performance and service life.
- Shaft shoulder and housing bore shoulder height: It is necessary to ensure that the height of the shaft shoulder and the bearing housing bore shoulder is sufficient to support the bearing ring, but not too high to hinder bearing installation or interfere with the fillet radius. The shoulder dimensions must be designed strictly in accordance with the recommendations in the bearing catalog.
- Lubrication: Sufficient and appropriate lubrication (grease lubrication or oil lubrication) must be provided, as lubrication has a great impact on service life.
6. Common Application Fields
Tapered roller bearings are widely used in occasions that need to bear combined radial and axial loads, especially where axial loads are large:
- Gearboxes (automobile transmissions, industrial reducers)
- Automobile axles (wheel hubs, differentials)
- Roll necks of rolling mills
- Mining machinery
- Construction machinery
- Agricultural machinery
- Pumps
- Cranes
- Some machine tool spindles
Post time: Aug-15-2025